description: that doesn't suck
Bitrix24 REST API client








- No bullshit
- ✨ Expressive API
- Strongly typed methods and requests results with TypeScript
- Handles records batching and rate limiting for you
- ❤️ Promise-based
Install
npm install @2bad/bitrix
Usage
使用 Bitrix API 端点和访问令牌初始化客户端并使用客户端来减轻您的 Bitrix 痛苦:
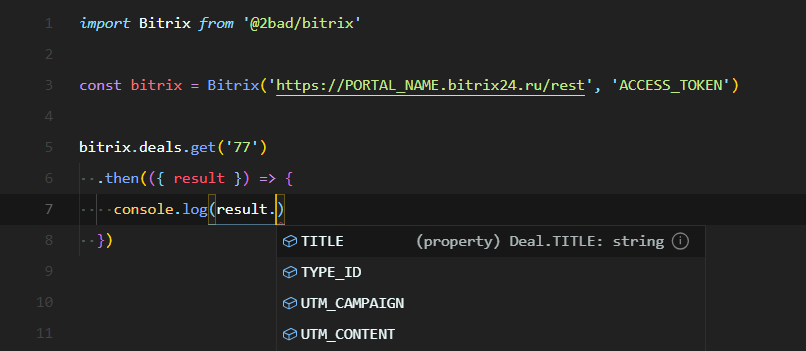
import Bitrix from '@2bad/bitrix'
const bitrix = Bitrix('https://PORTAL_NAME.bitrix24.ru/rest', 'ACCESS_TOKEN')
// Get deal
bitrix.deals.get('77')
.then(({ result }) => {
// Get typed payload
const { TITLE } = result // string
console.log(TITLE)
})
.catch(console.error)
// Get all deals
bitrix.deals.list({ select: ["*", "UF_*"] })
.then(({ result }) => {
const titles = result.map((e) => e.TITLE)
console.log(titles)
})
.catch(console.error)
Authentication
在您能够使用 Bitrix REST API 之前,您需要进行身份验证。
有两种方法可以做到这一点:
一种更难但正确的方法 — 创建一个 Bitrix 应用程序,然后使用 OAuth 进行身份验证。
使用 OAuth 进行身份验证需要一些额外的步骤,这取决于您使用 lambda 函数、某些服务器或 Postman 来处理它。
这将产生一个访问令牌。 使用它来初始化客户端:
const bitrix = Bitrix('https://PORTAL_NAME.bitrix24.ru/rest', 'ACCESS_TOKEN')
请注意,访问令牌仅存在 30 分钟,应使用 OAuth 刷新令牌提供的定期刷新,而 OAuth 刷新令牌又存在 1 个月。
更简单的方法 — 创建具有所需权限的 Bitrix 入站网络钩子。
它会立即为您提供一个端点,其中包含一个令牌。 使用它不需要额外的身份验证或访问令牌:
const bitrix = Bitrix('https://PORTAL_NAME.bitrix24.ru/rest/1/WEBHOOK_TOKEN')
该端点无限期存在。 庆幸并希望它不会适得其反。
API
How it works
客户端努力提供一致的、强类型的且同时毫不费力的体验。
它负责任何必要的批处理以运行“大型”命令,例如以尽可能少的网络请求检索所有交易或线索。 这允许使用一行代码实现每分钟读取 250,000 个条目并更新 5000 个条目。
如果需要应对每秒 2 个请求的 Bitrix REST API 限制,所有客户端方法都会自动进行速率限制和排队,因此您永远不会看到有关超过速率限制的 Bitrix 错误。
方法所需的参数和返回的负载类型根据Methods接口自动解析,有效描述所有当前支持的方法。
为了方便更好的架构,客户端分为几层:
- Methods — a mostly generic methods like
call to work with Bitrix API methods. They take care of the routine and provide a foundation for more complex operations.
- Client — a generic client, which takes care of some additional routine tasks like setting access token on every request, setting up a queue for the rate limiting, and providing generic methods.
- Services — each service provides an expressive interface to work with a specific group of Bitrix REST API operations. In essence, they do orchestrate generic client methods and parameters to get proper results.
- Bitrix client — a top-level provider of generic method and services. An effortless way to deal with Bitrix REST API by using an intuitive API, which takes care of all underlying complexity.
FAQ
完成了吗?
核心已准备就绪且稳定。 它可用于任意调用任何 Bitrix REST API 方法。
但是,并非所有 Bitrix REST API 方法都公开为方便的客户端服务(例如 bitrix.deals.list())。
如果您需要特定服务,请按照现有 的结构,通过提出合并请求来添加一个服务 和“添加新方法” 说明。
我不是 Typed Language Master Race 用户。 我可以将它与常规 JavaScript 一起使用吗?
当然。 只需像任何其他 NPM 模块一样安装和导入它。 但是 The Type Police 已经在路上了。
请注意,这个库在设计时并没有考虑到常规的 JavaScript,因此它不会进行不必要的动态检查。 不要太执着于传递错误的参数——它可能会产生意想不到的结果。 毕竟,TypeScript 是推荐的使用方式。
我应该检查负载 error 属性是否有错误吗?
你不应该。 相反,捕获拒绝,因为如果有效负载中存在任何错误,库将拒绝。
列表方法不返回用户字段!
默认情况下,Bitrix API 不会这样做。 在 select 参数中使用通配符以强制包含用户字段:
bitrix.deals.list({ select: ['*', 'UF_*'] })
用户字段输入不正确
客户端无法了解有效负载中的非默认属性。 因此,它假定任何有效载荷都可以具有 [key: string]: string 类型的任何其他字段:
bitrix.leads.get({ ID: '77' })
.then(({ result }) => {
// known property of type `string`
const title = result.TITLE
// unknown property of type `string`
const someData = result.UF_23232323
console.log(title, someData)
})
我需要调用一个尚不支持的 Bitrix 方法
使用适当的低级客户端带有转换的方法,如下所示:
bitrix.call('some.new.get' as any, { ID: '77' } as any)
.then((payload) => payload as GetPayload<NewPayload>)
bitrix.list('some.new.list' as any, { select: ["TITLE"] })
.then((payload) => payload as ListPayload<NewPayload>)
我需要调用一组特定的命令。 如何有效地做到这一点?
使用 batch 方法。 它将处理所有例程:
bitrix.batch({
lead: { method: Method.GET_LEAD, params: { ID: '77' } },
deals: { method: Method.LIST_DEALS, params: {} }
})
Development
npm test — run all tests and collect full coverage reportnpm run test:unit — run unit tests and collect coverage reportnpm run test:integration — run integration tests and collect coverage reportnpm run test:watch — watch for changes and run all testsnpm run test:unit:watch — watch for changes and run unit testsnpm run test:integration:watch — watch for changes and run integration testsnpm run build — build the library for the release
Adding new methods
正确的方法参数和有效负载类型处理在添加任何新方法时需要一些例程。 希望我们将来可以做得更好,但现在请遵循以下步骤:
- Add new method into the
Method enum.
- Add it into the
LISTABLE_METHODS array if it is listable (paginated). Not everything that lists is listable, so check it.
- Add or update related service:
- Put exposed by the service public methods into the
index.ts file. Ensure that you're properly mapping service method arguments to call or list params.
- Add related entities into the
entities.ts.
- Add interface describing service methods into the
methods.ts. Test and check method payload type to be sure you've described it correctly!
- Extend
Methods interface with the added service-specific interface. That way the client will know how to resolve parameters and payload types for the added method.
- Add tests into the
index.unit.test.ts.
- Re-export service public types like Entities in the bitrix.ts to make them available to the end-users.
- Document addition in the docs.
description: that doesn't suck
Bitrix24 REST API client








- ???? No bullshit
- ✨ Expressive API
- ???? Strongly typed methods and requests results with TypeScript
- ???? Handles records batching and rate limiting for you
- ❤️ Promise-based

Install
npm install @2bad/bitrix
Usage
Init client with Bitrix API endpoint and access token and use the client to ease your Bitrix pain:
import Bitrix from '@2bad/bitrix'
const bitrix = Bitrix('https://PORTAL_NAME.bitrix24.ru/rest', 'ACCESS_TOKEN')
// Get deal
bitrix.deals.get('77')
.then(({ result }) => {
// Get typed payload
const { TITLE } = result // string
console.log(TITLE)
})
.catch(console.error)
// Get all deals
bitrix.deals.list({ select: ["*", "UF_*"] })
.then(({ result }) => {
const titles = result.map((e) => e.TITLE)
console.log(titles)
})
.catch(console.error)
Authentication
Before you'll be able to use Bitrix REST API, you need to authenticate.
There are two ways to do that:
A harder, but proper way — create a Bitrix application and then authenticate with an OAuth.
Authentication with an OAuth requires some additional steps and that's up to you to deal with it using a lambda function, some server or a Postman.
That will yield an access token. Use it to init the client:
const bitrix = Bitrix('https://PORTAL_NAME.bitrix24.ru/rest', 'ACCESS_TOKEN')
Note, that access token lives only 30 minutes and should be refreshed periodically with provided by OAuth refresh token, which in turn lives 1 month.
An easier way — create a Bitrix inbound webhook with required permissions.
It will instantly give you an endpoint with a token inside of it. No additional authentication or access tokens required to use it:
const bitrix = Bitrix('https://PORTAL_NAME.bitrix24.ru/rest/1/WEBHOOK_TOKEN')
That endpoint lives indefinitely. Rejoice and hope that it won't backfire on you.
API
How it works
The client tries hard to provide a consistent, strongly typed and at the same time effortless experience.
It takes care of the any necessary batching to run "large" commands, like retrieving all deals or leads with least possible network request. That allows achieving a reading of the 250 000 and updating of 5000 entries per minute with a single line of code.
All client methods are automatically rate-limited and queued if needed to cope with Bitrix REST API limitation of 2 requests per second, so you should never see Bitrix errors about exceeding rate limits.
Methods required params and returned payload types are automatically resolved based on Methods interface, which effectively describes all currently supported methods.
To facilitate better architecture, the client divided into layers:
- Methods — a mostly generic methods like
call to work with Bitrix API methods. They take care of the routine and provide a foundation for more complex operations.
- Client — a generic client, which takes care of some additional routine tasks like setting access token on every request, setting up a queue for the rate limiting, and providing generic methods.
- Services — each service provides an expressive interface to work with a specific group of Bitrix REST API operations. In essence, they do orchestrate generic client methods and parameters to get proper results.
- Bitrix client — a top-level provider of generic method and services. An effortless way to deal with Bitrix REST API by using an intuitive API, which takes care of all underlying complexity.
FAQ
Is it finished?
The core is ready and stable. It can be used to arbitrary invoke any Bitrix REST API methods.
However, not all Bitrix REST API methods are exposed as convenient client services yet (the ones like bitrix.deals.list()).
If you need specific service, add one by making a Pull Request, following the structure of already existing services and "Adding new methods" instructions.
I'm not a Typed Language Master Race user. Can I use it with a regular JavaScript?
Sure. Just install and import it as any other NPM module. But The Type Police is already on the way for you.
Note that this library wasn't designed with regular JavaScript in mind, so it doesn't make unnecessary dynamic checks. Don't be too persistent in passing on wrong parameters — it might yield unexpected results. After all, TypeScript is a recommended way to use it.
Should I check payloads error properties for errors?
You shouldn't. Catch rejections instead, as the library will reject if there are any errors in a payload.
List method does not return user fields!
Bitrix API doesn't do that by default. Use wildcards in select param to force inclusion of user fields:
bitrix.deals.list({ select: ['*', 'UF_*'] })
User fields are not typed properly
Client can't know about non-default properties in payloads. Because of that, it assumes that any payload can have any additional fields of type [key: string]: string:
bitrix.leads.get({ ID: '77' })
.then(({ result }) => {
// known property of type `string`
const title = result.TITLE
// unknown property of type `string`
const someData = result.UF_23232323
console.log(title, someData)
})
I need to call a Bitrix method which isn't supported yet
Use appropriate low-level client methods with a casting, like so:
bitrix.call('some.new.get' as any, { ID: '77' } as any)
.then((payload) => payload as GetPayload<NewPayload>)
bitrix.list('some.new.list' as any, { select: ["TITLE"] })
.then((payload) => payload as ListPayload<NewPayload>)
I need to call a specific set of commands. How to do that effectively?
Use the batch method. It will handle all routine:
bitrix.batch({
lead: { method: Method.GET_LEAD, params: { ID: '77' } },
deals: { method: Method.LIST_DEALS, params: {} }
})
Development
npm test — run all tests and collect full coverage reportnpm run test:unit — run unit tests and collect coverage reportnpm run test:integration — run integration tests and collect coverage reportnpm run test:watch — watch for changes and run all testsnpm run test:unit:watch — watch for changes and run unit testsnpm run test:integration:watch — watch for changes and run integration testsnpm run build — build the library for the release
Adding new methods
Proper method parameters and payload types handling requires some routine when adding any new method. Hopefully, we can do it better in future, but for now follow those steps:
- Add new method into the
Method enum.
- Add it into the
LISTABLE_METHODS array if it is listable (paginated). Not everything that lists is listable, so check it.
- Add or update related service:
- Put exposed by the service public methods into the
index.ts file. Ensure that you're properly mapping service method arguments to call or list params.
- Add related entities into the
entities.ts.
- Add interface describing service methods into the
methods.ts. Test and check method payload type to be sure you've described it correctly!
- Extend
Methods interface with the added service-specific interface. That way the client will know how to resolve parameters and payload types for the added method.
- Add tests into the
index.unit.test.ts.
- Re-export service public types like Entities in the bitrix.ts to make them available to the end-users.
- Document addition in the docs.










