在 R 中叠加核分布
我试图在图中放置 3 个密度函数
plot(density(all_noise),xlim=c(-1,1),ylim=c(0,10))
lines(density(max_nearby),col="blue")
lines(density(max_repeats),col="red")
,我得到了 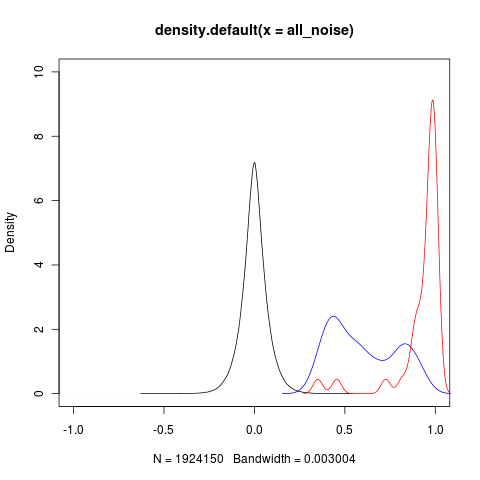
y 轴上的密度值不应该 <0 吗? 1?有没有更好的叠加方法 内核发行版?
str(density(all_noise))
List of 7
$ x : num [1:512] -0.629 -0.626 -0.624 -0.622 -0.62 ...
$ y : num [1:512] 1.41e-06 8.22e-06 3.16e-05 7.85e-05 1.24e-04 ...
$ bw : num 0.003
$ n : int 1924150
$ call : language density.default(x = all_noise)
$ data.name: chr "all_noise"
$ has.na : logi FALSE
- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"
str(density(max_nearby))
List of 7
$ x : num [1:512] 0.154 0.156 0.158 0.16 0.162 ...
$ y : num [1:512] 0.00111 0.00125 0.0014 0.00157 0.00175 ...
$ bw : num 0.0543
$ n : int 250
$ call : language density.default(x = max_nearby)
$ data.name: chr "max_nearby"
$ has.na : logi FALSE
- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"
str(density(max_repeats ))
List of 7
$ x : num [1:512] 0.272 0.274 0.275 0.277 0.279 ...
$ y : num [1:512] 0.00507 0.00607 0.00722 0.00854 0.01011 ...
$ bw : num 0.0261
$ n : int 34
$ call : language density.default(x = max_repeats)
$ data.name: chr "max_repeats"
$ has.na : logi FALSE
- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"
I am trying to place 3 density functions in plot using
plot(density(all_noise),xlim=c(-1,1),ylim=c(0,10))
lines(density(max_nearby),col="blue")
lines(density(max_repeats),col="red")
and I got
Shouldn't the density value on the y axis be < 1? Are there better methods for superimposing
kernel distributions?
str(density(all_noise))
List of 7
$ x : num [1:512] -0.629 -0.626 -0.624 -0.622 -0.62 ...
$ y : num [1:512] 1.41e-06 8.22e-06 3.16e-05 7.85e-05 1.24e-04 ...
$ bw : num 0.003
$ n : int 1924150
$ call : language density.default(x = all_noise)
$ data.name: chr "all_noise"
$ has.na : logi FALSE
- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"
str(density(max_nearby))
List of 7
$ x : num [1:512] 0.154 0.156 0.158 0.16 0.162 ...
$ y : num [1:512] 0.00111 0.00125 0.0014 0.00157 0.00175 ...
$ bw : num 0.0543
$ n : int 250
$ call : language density.default(x = max_nearby)
$ data.name: chr "max_nearby"
$ has.na : logi FALSE
- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"
str(density(max_repeats ))
List of 7
$ x : num [1:512] 0.272 0.274 0.275 0.277 0.279 ...
$ y : num [1:512] 0.00507 0.00607 0.00722 0.00854 0.01011 ...
$ bw : num 0.0261
$ n : int 34
$ call : language density.default(x = max_repeats)
$ data.name: chr "max_repeats"
$ has.na : logi FALSE
- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"
如果你对这篇内容有疑问,欢迎到本站社区发帖提问 参与讨论,获取更多帮助,或者扫码二维码加入 Web 技术交流群。

绑定邮箱获取回复消息
由于您还没有绑定你的真实邮箱,如果其他用户或者作者回复了您的评论,将不能在第一时间通知您!

发布评论
评论(2)
密度曲线下的面积为1,但它们可以超过1。我认为你这样做没有任何问题。出于我自己的目的,我要做的唯一更改是用值初始化绘图窗口,以便所有密度都在绘图窗口的范围内。
另外,关于之前的答案(我还不能发表评论)请注意, ylim 是 plot() 的参数,而不是 Density() 的参数> --- 它没有告诉
密度()做任何事情。The area under the density curves is 1, but they can exceed 1. I see nothing wrong with how you're doing this. For my own purposes about the only change I'd make would be to initialize the plot window with values so that all densities are in the bounds of the plot window.
Also, regarding the previous answer (I can't comment yet) notice that
ylimis an argument toplot(), not todensity()--- it's not tellingdensity()to do anything.核密度图不是直方图。这是一个例子:看一下密度函数的最小值和最大值以及数据的实际最小值和最大值。
kernel density plot is not a histogram. here is an example: take a look at the min and max of the density function and real min max of the data.