如何更新或同步 GitHub 上的分叉存储库?
我分叉了一个项目,进行了更改,并创建了一个已接受的拉取请求。新的提交后来被添加到存储库中。我如何将这些提交放入我的分叉中?
如果你对这篇内容有疑问,欢迎到本站社区发帖提问 参与讨论,获取更多帮助,或者扫码二维码加入 Web 技术交流群。

绑定邮箱获取回复消息
由于您还没有绑定你的真实邮箱,如果其他用户或者作者回复了您的评论,将不能在第一时间通知您!
我分叉了一个项目,进行了更改,并创建了一个已接受的拉取请求。新的提交后来被添加到存储库中。我如何将这些提交放入我的分叉中?

由于您还没有绑定你的真实邮箱,如果其他用户或者作者回复了您的评论,将不能在第一时间通知您!
接受 或继续使用网站,即表示您同意使用 Cookies 和您的相关数据。
发布评论
评论(30)
如果你设置你的上游。使用 git remote -v 检查,这样就足够了。
If you set your upstream. Check with
git remote -v, then this will suffice.克隆分叉存储库后,转到克隆所在的目录路径和 Git Bash 终端中的几行。
现在就可以开始了。主存储库中的所有更新更改都将推送到您的分支存储库中。
“fetch”命令对于保持项目最新状态是必不可少的:只有在执行“git fetch”时,您才会获悉同事推送到远程服务器的更改。
您仍然可以访问此处进行进一步查询
When you have cloned your forked repository, go to the directory path where your clone resides and the few lines in your Git Bash Terminal.
And there you are good to go. All updated changes in the main repository will be pushed into your fork repository.
The "fetch" command is indispensable for staying up-to-date in a project: only when performing a "git fetch" will you be informed about the changes your colleagues pushed to the remote server.
You can still visit here for further queries
Android Studio 现在已经学会了使用 GitHub fork 存储库(您甚至不必通过控制台命令添加“上游”远程存储库)。
打开菜单 VCS → Git
并注意最后两个弹出菜单项:
Rebase my GitHub fork
创建拉取请求
尝试一下。我使用第一个来同步我的本地存储库。无论如何,在单击“Rebase my GitHub fork”后,您将可以在 Android Studio 中访问父远程存储库(“上游”)的分支,并且您将能够轻松地使用它们。
(我使用带有“Git 集成”和“GitHub”插件的 Android Studio 3.0。)
Android Studio now has learned to work with GitHub fork repositories (you don't even have to add "upstream" remote repository by console command).
Open menu VCS → Git
And pay attention to the two last popup menu items:
Rebase my GitHub fork
Create Pull Request
Try them. I use the first one to synchronize my local repository. Anyway the branches from the parent remote repository ("upstream") will be accessible in Android Studio after you click "Rebase my GitHub fork", and you will be able to operate with them easily.
(I use Android Studio 3.0 with "Git integration" and "GitHub" plugins.)
如何在本地计算机上更新分叉存储库?
首先,检查您的远程/主控
您应该有起源和上游。例如:
之后转到 main:
并从上游合并到 main:
How to update your forked repo on your local machine?
First, check your remote/master
You should have origin and upstream. For example:
After that go to main:
and merge from upstream to main:
假设您的分叉是 https://github.com/me/foobar 并且原始存储库是 https://github.com/someone/foobar
访问https://github.com/me/foobar/compare/master...某人:大师
如果您看到绿色文本
能够合并,则按创建拉取请求在下一页上,滚动到页面底部并单击合并拉取请求 和确认合并。
使用此代码片段生成链接以同步您的分叉存储库:
Assuming your fork is https://github.com/me/foobar and original repository is https://github.com/someone/foobar
Visit https://github.com/me/foobar/compare/master...someone:master
If you see green text
Able to mergethen press Create pull requestOn the next page, scroll to the bottom of the page and click Merge pull request and Confirm merge.
Use this code snippet to generate link to sync your forked repository:
我想添加到 @krlmlr 回答。
最初,分叉存储库有一个名为:
master的分支。如果您正在开发新功能或修复,通常会创建一个新分支feature并进行更改。如果您希望分叉存储库与父存储库同步,您可以为 pull.yml) /pull" rel="nofollow noreferrer">拉取应用程序(在功能分支),如下所示:
这会保持分叉存储库的
master分支正常运行- 与父母约会回购。它通过合并分支存储库的master分支来保持分支存储库的feature分支的更新。这假设feature分支是包含配置文件的默认分支。这里有两种
mergemethods发挥作用,一种是hardreset,它有助于强制将分叉存储库的master分支中的更改与父存储库和另一种方法是merge。此方法用于合并您在feature分支中完成的更改以及由于master分支中强制同步而完成的更改。如果发生合并冲突,拉取应用程序将允许您在拉取请求期间选择下一步操作。您可以在此处阅读有关基本和高级配置以及各种
合并方法的信息。我目前正在我的分叉存储库此处中使用此配置,以确保请求增强< a href="https://stackoverflow.com/q/20700696/10155936">此处保持更新。
I would like to add on to @krlmlr's answer.
Initially, the forked repository has one branch named :
master. If you are working on a new feature or a fix, you would generally create a new branchfeatureand make the changes.If you want the forked repository to be in sync with the parent repository, you could set up a config file(
pull.yml) for the Pull app (in the feature branch), like this:This keeps the
masterbranch of the forked repo up-to-date with the parent repo. It keeps thefeaturebranch of the forked repo updated via themasterbranch of the forked repo by merging the same. This assumes that thefeaturebranch is the default branch which contains the config file.Here two
mergemethodsare into play, one ishardresetwhich helps force sync changes in themasterbranch of the forked repo with the parent repo and the other method ismerge. This method is used to merge changes done by you in thefeaturebranch and changes done due to force sync in themasterbranch. In case of merge conflict, the pull app will allow you to choose the next course of action during the pull request.You can read about basic and advanced configs and various
mergemethodshere.I am currently using this configuration in my forked repo here to make sure an enhancement requested here stays updated.
这取决于您的存储库的大小以及您如何分叉它。
如果它是一个相当大的存储库,您可能希望以特殊的方式管理它(例如删除历史记录)。基本上,您可以获取当前版本和上游版本之间的差异,提交它们,然后挑选回主版本。
尝试阅读这个。它描述了如何处理大型 Git 存储库以及如何使用最新更改将其上游。
That depends on the size of your repository and how you forked it.
If it's quite a big repository you may have wanted to manage it in a special way (e.g. drop history). Basically, you can get differences between current and upstream versions, commit them and then cherry pick back to master.
Try reading this one. It describes how to handle big Git repositories and how to upstream them with latest changes.
如果你想让你的 GitHub 分支与相应的上游保持同步,还有专门针对 GitHub 的 Probot 程序: https://probot.github.io/apps/pull/ 完成这项工作。
您需要允许在您的帐户中安装,它将使您的分叉保持最新状态。
If you want to keep your GitHub forks up to date with the respective upstreams, there also exists this probot program for GitHub specifically: https://probot.github.io/apps/pull/ which does the job.
You would need to allow installation in your account and it will keep your forks up to date.
尝试一下,单击“获取上游”以从上游主服务器同步您的分叉存储库。
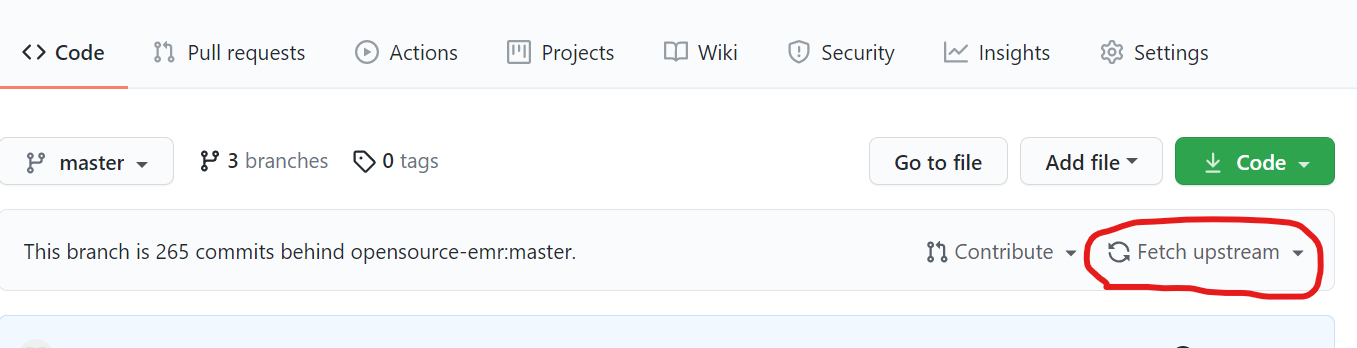
Try this, Click on "Fetch upstream" to sync your forked repo from upstream master.

如果使用 GitHub Desktop,只需 6 步(实际上只有 5 步)即可轻松完成。
打开 Github Desktop 并选择存储库后,
来自父存储库的上游分支)
分支)
任何提交以查看更改。
master/branch-name中单击“合并”。以下面的 GIF 为例:
If you use GitHub Desktop, you can do it easily in just 6 steps (actually only 5).
Once you open Github Desktop and choose your repository,
upstream branches from parent repository)
branch)
any commit to see the changes.
master/branch-name, based on your active branch.Checkout the GIF below as an example:
使用这些命令(幸运的话)
Use these commands (in lucky case)
保持分叉存储库始终更新有两个主要因素。
因此,当您的拉取请求被接受时,您可以安全地删除该分支,因为当您使用上游更新它时,您贡献的代码将存在于分叉存储库的主版本中。这样你的master将始终处于干净的状态来创建一个新的分支来进行另一个更改。
这可以通过 cron 来完成。如果您在 Linux 中执行此操作,这里是示例代码。
将此代码放在
crontab 文件中以每小时执行一次作业。然后创建 cron.sh 脚本文件和 git 交互与ssh-agent和/或预计如下
检查您的分叉存储库。有时它总是会显示此通知:
There are two main things on keeping a forked repository always update for good.
So when your Pull Request is accepted then you can safely delete the branch as your contributed code will be then live in your master of your forked repository when you update it with the upstream. By this your master will always be in clean condition to create a new branch to do another change.
This can be done with cron. Here is for an example code if you do it in linux.
put this code on the
crontab fileto execute the job in hourly basis.then create the
cron.shscript file and a git interaction with ssh-agent and/or expect as belowCheck your forked repository. From time to time it will always show this notification:
可能有更微妙的选择,但这是我确信我的本地存储库与上游相同的唯一方法。
There may be subtler options, but it is the only way that I have any confidence that my local repository is the same as upstream.
在分叉存储库的本地克隆中,您可以将原始 GitHub 存储库添加为“远程”存储库。 (“Remotes”就像存储库 URL 的昵称 - 例如,
origin就是其中之一。)然后,您可以从该上游存储库获取所有分支,并重新调整您的工作以继续在上游工作版本。就命令而言,可能如下所示:如果您不想重写主分支的历史记录(例如,因为其他人可能已经克隆了它),那么您应该将最后一个命令替换为 git merge upper/主要。然而,为了进一步发出尽可能干净的拉取请求,最好进行变基。
如果您已将分支重新设置为
upstream/main,您可能需要强制推送才能将其推送到 GitHub 上您自己的分叉存储库。您可以这样做:您只需在重新设置基础后第一次使用
-f即可。In your local clone of your forked repository, you can add the original GitHub repository as a "remote". ("Remotes" are like nicknames for the URLs of repositories -
originis one, for example.) Then you can fetch all the branches from that upstream repository, and rebase your work to continue working on the upstream version. In terms of commands that might look like:If you don't want to rewrite the history of your main branch, (for example because other people may have cloned it) then you should replace the last command with
git merge upstream/main. However, for making further pull requests that are as clean as possible, it's probably better to rebase.If you've rebased your branch onto
upstream/mainyou may need to force the push in order to push it to your own forked repository on GitHub. You'd do that with:You only need to use the
-fthe first time after you've rebased.从 2014 年 5 月开始,可以直接从 GitHub 更新分支。截至 2017 年 9 月,这仍然有效,但是它将导致脏的提交历史记录。
从原始内容更新)。现在您有三个选项,但每个选项都会导致不太干净的提交历史记录。
Thisbranch is X commits advance, Y commits Behind <原始叉子>。所以,是的,您可以使用 GitHub Web UI 更新您的存储库及其上游,但这样做会玷污您的提交历史记录。坚持使用命令行 - 它是简单的。
Starting in May 2014, it is possible to update a fork directly from GitHub. This still works as of September 2017, BUT it will lead to a dirty commit history.
Update from original).Now you have three options, but each will lead to a less-than-clean commit history.
This branch is X commits ahead, Y commits behind <original fork>.So yes, you can keep your repo updated with its upstream using the GitHub web UI, but doing so will sully your commit history. Stick to the command line instead - it's easy.
以下是 GitHub 关于同步分叉的官方文档:
Here is GitHub's official document on Syncing a fork:
许多答案最终都会将您的分叉提前一次提交移到父存储库之前。此答案总结了此处找到的步骤,这些步骤将将您的分叉移动到与父级相同的提交。
将目录更改为本地存储库。
git remote add uppergit fetch uploadedIssue
git rebase upper/master代码>git status来检查是否提交了要合并的内容Issue
git Push origin master有关这些命令的更多信息,请参阅步骤 3。
A lot of answers end up moving your fork one commit ahead of the parent repository. This answer summarizes the steps found here which will move your fork to the same commit as the parent.
Change directory to your local repository.
git checkout masterAdd the parent as a remote repository,
git remote add upstream <repo-location>git fetch upstreamIssue
git rebase upstream/mastergit statusIssue
git push origin masterFor more information about these commands, refer to step 3.
如果像我一样,您从不直接向 master 提交任何内容(您确实应该这么做),那么您可以执行以下操作。
从您的分支的本地克隆中,创建您的上游远程。您只需要执行一次:
然后每当您想要赶上上游存储库 master 分支时,您需要:
假设您自己从未在 master 上提交过任何内容,那么您应该已经完成了。现在,您可以将本地 master 推送到原始远程 GitHub 分支。您还可以在当前最新的本地主分支上重新建立您的开发分支。
经过初始上游设置和主节点签出后,您所需要做的就是运行以下命令将主节点与上游同步:git pull upper upper master。
If, like me, you never commit anything directly to master, which you should really, you can do the following.
From the local clone of your fork, create your upstream remote. You only need to do that once:
Then whenever you want to catch up with the upstream repository master branch you need to:
Assuming you never committed anything on master yourself you should be done already. Now you can push your local master to your origin remote GitHub fork. You could also rebase your development branch on your now up-to-date local master.
Past the initial upstream setup and master checkout, all you need to do is run the following command to sync your master with upstream: git pull upstream master.
前言:您的分叉是“源”,您分叉的存储库是“上游”。
假设您已经使用如下命令将分叉克隆到计算机上:
如果给出了该命令,则需要按以下顺序继续:
将“上游”添加到克隆的存储库中( “起源”):
从“上游”获取提交(和分支):
切换到分支的“master”分支(“源”):
存储“master”分支的更改:
将“上游”的“master”分支的更改合并到“源”的“master”分支:
解决合并冲突(如果有)并提交合并
将更改推送到您的分支
<前><代码>git推送
取回您隐藏的更改(如果有)
您完成了!恭喜!
GitHub 还提供了有关此主题的说明:同步 fork
Foreword: Your fork is the "origin" and the repository you forked from is the "upstream".
Let's assume that you cloned already your fork to your computer with a command like this:
If that is given then you need to continue in this order:
Add the "upstream" to your cloned repository ("origin"):
Fetch the commits (and branches) from the "upstream":
Switch to the "master" branch of your fork ("origin"):
Stash the changes of your "master" branch:
Merge the changes from the "master" branch of the "upstream" into your the "master" branch of your "origin":
Resolve merge conflicts if any and commit your merge
Push the changes to your fork
Get back your stashed changes (if any)
You're done! Congratulations!
GitHub also provides instructions for this topic: Syncing a fork
可以通过三种方式执行此操作:从 Web UI(选项 1)、从 GitHub CLI(选项 2)或从命令行(选项 3)。
选项 1 - 网页用户界面
选项 2 - GitHub CLI
要从其父级更新远程分叉,请使用
gh reposync子命令并提供您的分叉名称作为参数。如果上游存储库的更改导致冲突,则 GitHub CLI 无法同步。您可以设置
-force标志来覆盖目标分支。如何安装 GitHub CLI
GitHub CLI 手册
选项 3 - 命令行
在将一个分支与某个分支同步之前上游存储库,必须 在 Git 中配置指向上游存储库的远程。
1 打开 Git Bash。
2 将当前工作目录更改为本地项目。
3 从上游存储库获取分支及其各自的提交。对 BRANCHNAME 的提交将存储在本地分支上游/BRANCHNAME 中。
4 检查您的 fork 的本地默认分支 - 在本例中,我们使用 main。
5 将上游默认分支(在本例中为上游/主分支)中的更改合并到本地默认分支中。这将使您的分支的默认分支与上游存储库同步,而不会丢失本地更改。
如果本地分支没有任何唯一提交,Git 将执行“快进”:
来源:GitHub 文档- 同步分支
@Paebbels 实现选项 2
在您的用户空间/GitHub 组织中创建一个存储库,并添加单个 YAML 文件以及多个*.repos 文件。/=:branch[,branch]*
_All.repos引用其他*.repos文件(存储库组)。语法如下:.github/workflows /Synchronize.ymlThere are three ways one can do that: from the web UI (Option 1), from the GitHub CLI (Option 2), or from the command line (Option 3).
Option 1 - Web UI
Option 2 - GitHub CLI
To update the remote fork from its parent, use the
gh repo syncsubcommand and supply your fork name as argument.If the changes from the upstream repository cause conflict then the GitHub CLI can't sync. You can set the
-forceflag to overwrite the destination branch.How to Install GitHub CLI
GitHub CLI Manual
Option 3 - Command Line
Before syncing one's fork with an upstream repository, one must configure a remote that points to the upstream repository in Git.
1 Open Git Bash.
2 Change the current working directory to your local project.
3 Fetch the branches and their respective commits from the upstream repository. Commits to BRANCHNAME will be stored in the local branch upstream/BRANCHNAME.
4 Check out your fork's local default branch - in this case, we use main.
5 Merge the changes from the upstream default branch - in this case, upstream/main - into your local default branch. This brings your fork's default branch into sync with the upstream repository, without losing your local changes.
If one's local branch didn't have any unique commits, Git will instead perform a "fast-forward":
Source: GitHub Docs - Syncing a fork
Implementation of Option 2 by @Paebbels
Create a repository in your userspace / GitHub organisation and add a single YAML file as well as multiple *.repos files. The
_All.reposrefers to other*.reposfiles (repository groups). The syntax is as follows:<upstream-org>/<upstream-repo>=<local-repo>:branch[,branch]*.github/workflows/Synchronize.yml_ALL.reposOSVVM.repos_Others.repos\r\n' read -r organisation; do echo "${organisation}" while IFS=
\r\n' read -r line; do
parent=${line%=*}
fork=${line#*=}
repo=${fork%:*}
branches=${fork#*:}
branches=(${branches//,/ })
echo " ${parent} => ${repo}"
for branch in "${branches[@]}"; do
echo " gh repo sync $GitHubUser/${repo} -b ${branch}"
gh repo sync $GitHubUser/${repo} -b ${branch} || true
done
done < <(cat "${organisation}.repos")
done < <(cat "_ALL.repos")
_ALL.reposOSVVM.repos_Others.repos_ALL.reposOSVVM.repos_Others.reposGitHub 现在引入了一项功能,只需单击按钮即可同步分叉。
转到您的分叉,单击
获取上游,然后单击获取并合并直接同步您的分叉及其父仓库。您还可以在合并之前点击
比较按钮来比较更改。参考:GitHub 的 文档
GitHub has now introduced a feature to sync a fork with the click of a button.
Go to your fork, click on
Fetch upstream, and then click onFetch and mergeto directly sync your fork with its parent repo.You may also click on the
Comparebutton to compare the changes before merging.Reference: GitHub's documentation
自 2013 年 11 月以来,GitHub 提出了一个非官方功能请求,要求他们添加一个非常简单直观的方法来保持本地分支与上游同步:
https://github.com/isaacs/github/issues/121
注意:由于该功能请求是非官方的,因此建议联系
[email protected]将您对此类功能的支持添加到予以实施。上述非官方功能请求可以用作对此实施的兴趣程度的证据。Since November 2013 there has been an unofficial feature request open with GitHub to ask them to add a very simple and intuitive method to keep a local fork in sync with upstream:
https://github.com/isaacs/github/issues/121
Note: Since the feature request is unofficial it is also advisable to contact
[email protected]to add your support for a feature like this to be implemented. The unofficial feature request above could be used as evidence of the amount of interest in this being implemented.截至本答案发布之日,GitHub 还没有(或者我应该说不再了吗?) Web 界面中的此功能。不过,您可以询问
[电子邮件受保护]对此添加您的投票。与此同时,GitHub 用户 bardiharborow 创建了一个工具来执行此操作:
https://upriver.github.io/
来源在这里:https://github.com/upriver/upriver.github.io
As of the date of this answer, GitHub has not (or shall I say no longer?) this feature in the web interface. You can, however, ask
[email protected]to add your vote for that.In the meantime, GitHub user bardiharborow has created a tool to do just this:
https://upriver.github.io/
Source is here: https://github.com/upriver/upriver.github.io
如果您使用的是 Windows 或 Mac 版 GitHub,那么现在他们具有更新分支的一键功能:
If you are using GitHub for Windows or Mac then now they have a one-click feature to update forks:
实际上,可以从浏览器中上游的任何提交在分支中创建分支:
https://github.com//commits/ ,其中,repo 是您的分叉,hash 是提交的完整哈希值,您可以在上游 Web 界面中找到它。例如,我可以打开 https://github.com/max630/linux/commits/0aa0313f9d576affd7747cc3f179feb097d28990,在撰写本文时指向linuxmaster。然后,您可以将该分支提取到本地克隆,并且当您在此基础上进行编辑 犯罪。或者使用 Web 界面更改该分支中的某些内容。
它是如何工作的(这是一个猜测,我不知道 GitHub 到底是如何做到的):分叉共享对象存储并使用 命名空间来分隔用户的引用。因此,您可以通过分叉访问所有提交,即使它们在分叉时不存在。
Actually, it is possible to create a branch in your fork from any commit of the upstream in the browser:
https://github.com/<repo>/commits/<hash>, where repo is your fork, and hash is full hash of commit which you can find in the upstream web interface. For example, I can open https://github.com/max630/linux/commits/0aa0313f9d576affd7747cc3f179feb097d28990, which points tolinuxmasteras time of writing.You can then fetch that branch to your local clone, and you won't have to push all that data back to GitHub when you push edits on top of that commit. Or use the web interface to change something in that branch.
How it works (it is a guess, I don't know how exactly GitHub does it): forks share object storage and use namespaces to separate users' references. So you can access all commits through your fork, even if they did not exist by the time of forking.
请按照以下步骤操作。我尝试过它们,它对我有帮助。
到您的分行结帐
拉取源存储库分支以获取最新代码
Follow the below steps. I tried them and it helped me.
Checkout to your branch
Pull source repository branch for getting the latest code
我用这一行更新我的分叉存储库:
如果您不想向项目添加另一个远程端点,请使用此行,正如此处发布的其他解决方案一样。
I update my forked repos with this one line:
Use this if you dont want to add another remote endpoint to your project, as other solutions posted here.
作为对这个答案的补充,我一直在寻找一种从上游分支一次性更新我的克隆存储库(来源)的所有远程分支的方法。我就是这样做的。
这假设您已经配置了一个指向源存储库的上游远程(其中起源是从其分叉的),并将其与
git fetch上游同步。然后运行:
此命令的第一部分列出上游远程存储库中的所有头,并删除 SHA-1 后跟
refs/heads/分支名称前缀。然后,对于每个分支,它将上游远程跟踪分支(本地端的
refs/remotes/upstream/)的本地副本直接推送到源上的远程分支(refs/heads/在远程端)。这些分支同步命令中的任何一个都可能因以下两个原因之一而失败:上游分支已被重写,或者您已将该分支上的提交推送到您的分支。在第一种情况下,如果您没有向分支上的分支提交任何内容,则可以安全地强制推送(添加 -f 开关;即
git push -f上面的命令)。在另一种情况下,这是正常的,因为您的分叉分支已经分叉,并且在您的提交合并回上游之前,您不能指望同步命令起作用。上游。As a complement to this answer, I was looking for a way to update all remote branches of my cloned repo (origin) from upstream branches in one go. This is how I did it.
This assumes you have already configured an upstream remote pointing at the source repository (where origin was forked from) and have synced it with
git fetch upstream.Then run:
The first part of this command lists all heads in the upstream remote repo and removes the SHA-1 followed by
refs/heads/branch name prefix.Then for each of these branches, it pushes the local copy of the upstream remote tracking branch (
refs/remotes/upstream/<branch>on local side) directly to the remote branch on origin (refs/heads/<branch>on remote side).Any of these branch sync commands may fail for one of two reasons: either the upstream branch have been rewritten, or you have pushed commits on that branch to your fork. In the first case where you haven't committed anything to the branch on your fork it is safe to push forcefully (Add the -f switch; i.e.
git push -fin the command above). In the other case this is normal as your fork branch have diverged and you can't expect the sync command to work until your commits have been merged back into upstream.“Pull”应用是一种自动设置并忘记的解决方案。它将把你的分支的默认分支与上游存储库同步。
访问该 URL,单击绿色的“安装”按钮,然后选择要启用自动同步的存储库。
该分支每小时直接在 GitHub 上更新一次,在本地计算机上,您需要拉取 master 分支以确保本地副本同步。
The "Pull" app is an automatic set-up-and-forget solution. It will sync the default branch of your fork with the upstream repository.
Visit the URL, click the green "Install" button and select the repositories where you want to enable automatic synchronization.
The branch is updated once per hour directly on GitHub, on your local machine you need to pull the master branch to ensure that your local copy is in sync.