查找所有使用 easy_install/pip 安装的软件包?
有没有办法找到所有使用 easy_install 或 pip 安装的 Python PyPI 包?我的意思是,排除使用发行版工具安装的所有内容(在本例中是 Debian 上的 apt-get)。
Is there a way to find all Python PyPI packages that were installed with easy_install or pip? I mean, excluding everything that was/is installed with the distributions tools (in this case apt-get on Debian).
如果你对这篇内容有疑问,欢迎到本站社区发帖提问 参与讨论,获取更多帮助,或者扫码二维码加入 Web 技术交流群。

绑定邮箱获取回复消息
由于您还没有绑定你的真实邮箱,如果其他用户或者作者回复了您的评论,将不能在第一时间通知您!


发布评论
评论(19)
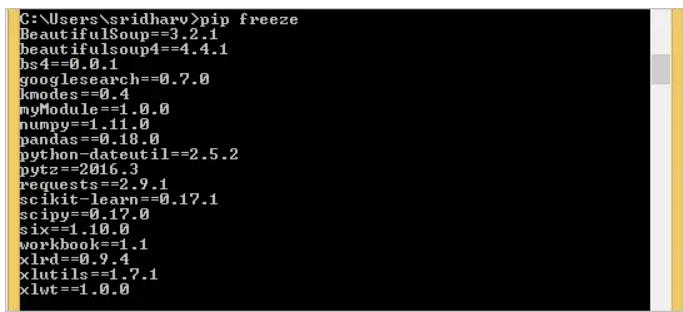
pip freeze将输出已安装的软件包及其版本的列表。它还允许您将这些包写入一个文件,稍后可用于设置新环境。https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/reference/ pip_freeze/#pip-freeze
pip freezewill output a list of installed packages and their versions. It also allows you to write those packages to a file that can later be used to set up a new environment.https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/reference/pip_freeze/#pip-freeze
从 pip 1.3 版本开始,您现在可以使用
pip list它有一些有用的选项,包括显示过时的包的能力。这是文档:https://pip.pypa.io/en/latest/reference/pip_list/
As of version 1.3 of pip you can now use
pip listIt has some useful options including the ability to show outdated packages. Here's the documentation: https://pip.pypa.io/en/latest/reference/pip_list/
如果有人想知道你可以使用“pip show”命令。
这将列出给定包的安装目录。
If anyone is wondering you can use the 'pip show' command.
This will list the install directory of the given package.
开始于:
列出所有包。找到所需的包后,请使用:
这将显示有关该包的详细信息,包括其文件夹。如果您已经知道包名称,则可以跳过第一部分
单击 此处了解有关 pip show 和 此处了解有关 pip list 的更多信息。
例子:
Start with:
To list all packages. Once you found the package you want, use:
This will show you details about this package, including its folder. You can skip the first part if you already know the package name
Click here for more information on pip show and here for more information on pip list.
Example:
如果 Debian 在
pip install默认目标方面表现得像最近的 Ubuntu 版本,那就非常简单了:它安装到/usr/local/lib/而不是/usr/lib(apt默认目标)。检查https://askubuntu.com/questions/173323/how-do-i-detect-and-remove-python-packages-installed-via-pip/259747#259747我是一名 ArchLinux 用户,当我尝试 pip 时,我遇到了同样的问题。这是我在 Arch 中解决这个问题的方法。
这里的关键是
/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages,这是 pip 安装到的目录,YMMV。pacman -Qo是 Arch 的 pac kage man ager 检查文件所有权的方式。No package是当没有包拥有该文件时返回的一部分:error: No package owns $FILENAME。棘手的解决方法:我正在查询__init__.py,因为pacman -Qo在目录方面有点无知:(为了对其他发行版做到这一点,你必须找出
pip在哪里安装东西(只是sudo pip install东西),如何查询文件的所有权(Debian/Ubuntu 方法是dpkg -S)以及“没有软件包拥有该路径”的返回值(Debian/Ubuntu 是没有找到匹配模式的路径Debian/Ubuntu 用户,请注意:dpkg -如果您给它一个符号链接,S将失败,只需首先使用realpath解决它:Fedora 用户可以尝试(感谢 @eddygeek):
If Debian behaves like recent Ubuntu versions regarding
pip installdefault target, it's dead easy: it installs to/usr/local/lib/instead of/usr/lib(aptdefault target). Check https://askubuntu.com/questions/173323/how-do-i-detect-and-remove-python-packages-installed-via-pip/259747#259747I am an ArchLinux user and as I experimented with pip I met this same problem. Here's how I solved it in Arch.
Key here is
/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages, which is the directory pip installs to, YMMV.pacman -Qois how Arch's pac kage man ager checks for ownership of the file.No packageis part of the return it gives when no package owns the file:error: No package owns $FILENAME. Tricky workaround: I'm querying about__init__.pybecausepacman -Qois a little bit ignorant when it comes to directories :(In order to do it for other distros, you have to find out where
pipinstalls stuff (justsudo pip installsomething), how to query ownership of a file (Debian/Ubuntu method isdpkg -S) and what is the "no package owns that path" return (Debian/Ubuntu isno path found matching pattern). Debian/Ubuntu users, beware:dpkg -Swill fail if you give it a symbolic link. Just resolve it first by usingrealpath. Like this:Fedora users can try (thanks @eddygeek):
新版本的 pip 能够通过
pip list -l或pip freeze -l(--list) 执行 OP 想要的操作。在 Debian 上(至少),手册页没有明确说明这一点,我只是在假设该功能必须存在的情况下使用
pip list --help发现了它。最近有评论表明此功能在文档或现有答案中并不明显(尽管有些人暗示过),所以我认为我应该发布。我更愿意这样做作为评论,但我没有声誉点。
Newer versions of pip have the ability to do what the OP wants via
pip list -lorpip freeze -l(--list).On Debian (at least) the man page doesn't make this clear, and I only discovered it - under the assumption that the feature must exist - with
pip list --help.There are recent comments that suggest this feature is not obvious in either the documentation or the existing answers (although hinted at by some), so I thought I should post. I would have preferred to do so as a comment, but I don't have the reputation points.
pip.get_installed_distributions()将给出已安装软件包的列表pip.get_installed_distributions()will give a list of installed packages添加@Paul Woolcock的答案,
将创建一个需求文件,其中包含所有已安装软件包以及当前位置活动环境中已安装的版本号。运行
将安装需求文件中指定的包。
Adding to @Paul Woolcock's answer,
will create a requirements file with all installed packages along with the installed version numbers in the active environment at the current location. Running
will install the packages specified in the requirements file.
下面的代码有点慢,但它提供了
pip可以识别的格式良好的包列表。也就是说,并非所有这些都是由 pip“安装”的,但所有这些都应该能够由 pip 升级。它慢的原因是它列出了整个 pypi 存储库的内容。我提交了票据建议
pip list提供类似的功能,但是更有效。示例输出:(将搜索限制为子集,而不是全部搜索“.”。)
The below is a little slow, but it gives a nicely formatted list of packages that
pipis aware of. That is to say, not all of them were installed "by" pip, but all of them should be able to be upgraded by pip.The reason it is slow is that it lists the contents of the entire pypi repo. I filed a ticket suggesting
pip listprovide similar functionality but more efficiently.Sample output: (restricted the search to a subset instead of '.' for all.)
请注意,如果您的计算机上安装了多个版本的 Python,则每个版本可能会关联多个 pip 版本。
根据您的关联,您可能需要非常谨慎地使用 pip 命令:
为我工作,我正在运行 Python3.4。仅使用
pip list返回错误程序“pip”当前未安装。您可以通过键入:sudo apt-get install python-pip来安装它。Take note that if you have multiple versions of Python installed on your computer, you may have a few versions of pip associated with each.
Depending on your associations, you might need to be very cautious of what pip command you use:
Worked for me, where I'm running Python3.4. Simply using
pip listreturned the errorThe program 'pip' is currently not installed. You can install it by typing: sudo apt-get install python-pip.正如 @almenon 指出的,这不再有效,并且它不是在代码中获取包信息的受支持的方法。以下情况会引发异常:
要实现此目的,您可以导入
pkg_resources。这是一个示例:我使用的是
v3.6.5As @almenon pointed out, this no longer works and it is not the supported way to get package information in your code. The following raises an exception:
To accomplish this, you can import
pkg_resources. Here's an example:I'm on
v3.6.5pip freeze 列出所有已安装的软件包,即使不是通过 pip/easy_install 进行安装的。
在 CentOs/Redhat 上发现通过 rpm 安装的软件包。
pip freeze lists all installed packages even if not by pip/easy_install.
On CentOs/Redhat a package installed through rpm is found.
以下是用于 fedora 或其他 rpm 发行版的单行代码(基于 @barraponto 提示):
将其附加到上一个命令以获得更清晰的输出:
Here is the one-liner for fedora or other rpm distros (based on @barraponto tips):
Append this to the previous command to get cleaner output:
获取
site-packages/中的所有文件/文件夹名称(以及dist-packages/如果存在),并使用包管理器删除通过包安装的文件/文件夹名称。Get all file/folder names in
site-packages/(anddist-packages/if it exists), and use your package manager to strip the ones that were installed via package.如果您使用 Anaconda python 发行版,则可以使用
conda list命令查看通过什么方法安装的内容:获取通过
pip安装的条目code> (可能包括pip本身):当然,您可能只想选择第一列,您可以使用它(如果需要,不包括
pip):最后您可以获取这些值并使用以下命令 pip uninstall 全部:
请注意使用
-y标志进行pip uninstall以避免必须确认删除。If you use the Anaconda python distribution, you can use the
conda listcommand to see what was installed by what method:To grab the entries installed by
pip(including possiblypipitself):Of course you probably want to just select the first column, which you can do with (excluding
pipif needed):Finally you can grab these values and pip uninstall all of them using the following:
Note the use of the
-yflag for thepip uninstallto avoid having to give confirmation to delete.对于那些没有安装 pip 的人,我在 github 上找到了这个快速脚本(适用于Python 2.7.13):
For those who don't have pip installed, I found this quick script on github (works with Python 2.7.13):
点列表[选项]
您可以在此处查看完整参考
pip list [options]
You can see the complete reference here
至少对于 Ubuntu(也许还有其他)可以这样做(受到本线程中之前的 帖子 的启发):
At least for Ubuntu (maybe also others) works this (inspired by a previous post in this thread):
pip list:
这将获取已安装软件包的列表及其尖括号中的版本
pip List 有多个选项,例如
列出过时的软件包
这将列出 python 中安装的所有过时的软件包。
列出所有更新的包
这将列出所有最新的软件包。
列出没有依赖项的过时软件包
这将列出所有不依赖于其他包的过时包。
以json格式列出所有包
有关更多详细信息,请参阅:https://www .datasciencemadesimple.com/list-packages-modules-installed-python/
pip freeze:
我们还可以使用
这将获取已安装软件包的列表及其版本,如下所示
pip list:
This will get the list of installed packages along with their version in angular braces
pip List has multiple options like
List outdated packages
This will List all outdated packages installed in python.
List all updated packages
This will list all package that are upto date.
List outdated packages with no dependencies
This will List all outdated packages that are not dependencies of other packages.
List all the packages in json format
For More details Refer : https://www.datasciencemadesimple.com/list-packages-modules-installed-python/
pip freeze:
We can Also use
This will get the list of installed packages along with their version as shown below
