Matlab中使用滑块旋转图像
我在 Matlab 中有一个 GUI(使用 GUIDE),它看起来是这样的:
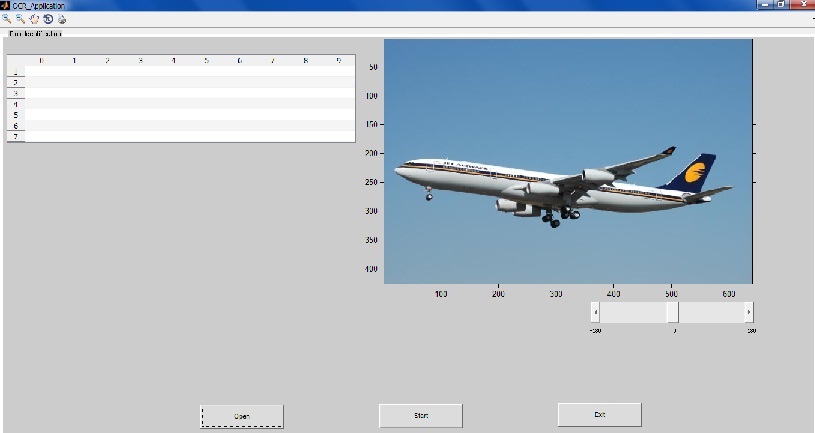
我想旋转使用滑块进行图像并实时显示变化。
我使用轴来显示图像。
我该怎么做?
编辑:我正在构建 OCR 应用程序。这就是我旋转盘子时的样子,数字完全变形了。

谢谢。
I have a GUI (using GUIDE) in Matlab, this is how it looks:

I want to rotate the image using slider and to show the change in real time.
I use axes to display the image.
how can I do this?
EDIT: I'm building OCR application. this is how the plate looks when I'm rotate it, the numbers are totally deformed.

thanks.
如果你对这篇内容有疑问,欢迎到本站社区发帖提问 参与讨论,获取更多帮助,或者扫码二维码加入 Web 技术交流群。

绑定邮箱获取回复消息
由于您还没有绑定你的真实邮箱,如果其他用户或者作者回复了您的评论,将不能在第一时间通知您!


发布评论
评论(1)
以下是 GUI 示例:
如果您希望在 GUIDE 中构建 GUI,请按照以下步骤操作:
创建GUI,并添加必要的组件:轴、滑块、静态文本(拖放)
使用“属性检查器”,根据需要更改滑块属性::
Min/Max/Value/SliderStep。如果您分配一个标签以便能够在代码中查找组件,也会有所帮助。在图中的
xxxx_OpeningFcn函数中,读取图像并将其存储在handles结构中,然后显示出来:handles.I = imread('cameraman.tif'); imshow(I, 'Parent',findobj(hObject,'Tag','imgAxis')) %# use tag you assigned guidata(hObject, handles); %# Update handles structureangle = round( get(hObject,'Value') ); imshow( imrotate(handles.I,angle) )编辑:
图像旋转是一种仿射变换,它将输入图像像素的位置 (x,y) 映射到输出图像的新坐标 (x2,y2)。问题是输出坐标可能并不总是整数。由于数字图像是在离散像素网格上表示的,因此采用了某种形式的重采样/插值(这就是为什么直线在以某些角度旋转时可能看起来呈锯齿状)。
(插图借自:了解数字图像插值)
Here is an example GUI:
If you prefer to build the GUI in GUIDE, follow these steps:
create GUI, and add necessary components: axis, slider, static text (drag-and-drop)
Using the "Property Inspector", change slider properties as required::
Min/Max/Value/SliderStep. Also would help if you assign aTagto be able to find components in the code.In the figure's
xxxx_OpeningFcnfunction, read and store the image in thehandlesstructure, then show it:handles.I = imread('cameraman.tif'); imshow(I, 'Parent',findobj(hObject,'Tag','imgAxis')) %# use tag you assigned guidata(hObject, handles); %# Update handles structureangle = round( get(hObject,'Value') ); imshow( imrotate(handles.I,angle) )EDIT:
Image rotation is an affine transformation which maps the position (x,y) of input image pixels onto new coordinates (x2,y2) for the output image. The problem is that the output coordinates may not always be integers. Since digital images are represented on a grid of discrete pixels, thus some form of resampling/interpolation is employed (which is why straight lines might look jagged when rotated at certain angles).
(Illustration borrowed from: Understanding Digital Image Interpolation)