- 教程
- 概述
- Environment Setup
- 语法
- 变量
- Commands
- M-Files
- 数据类型
- 运算符
- Decisions
- 循环
- Vectors
- Matrix
- Arrays
- Colon Notation
- Numbers
- Strings
- Functions
- Data Import
- Data Output
- Plotting
- Graphics
- Algebra
- Calculus
- Differential
- Integration
- Polynomials
- Transforms
- GNU Octave
- Simulink
- 有用的资源
- 讨论
- Show 例子 1
- Show 例子 2
- Show 例子 3
- Show 例子 4
- Show 例子 5
- if ... end statement
- if...else...end statement
- if...elseif...else statement
- 嵌套 if 语句(nested if statements)
- switch statement
- 嵌套的 switch 语句(nested switch statements)
- while 循环
- for 循环
- nested 循环
- break statement
- continue statement
- 载体的加法和减法(Addition and Subtraction of Vectors)
- 向量的标量乘法(Scalar Multiplication of Vectors)
- 矢量的转置(Transpose of a Vector)
- 附加向量(Appending Vectors)
- 矢量的大小(Magnitude of a Vector)
- 矢量点产品(Vector Dot Product)
- Vectors with Uniformly Spaced Elements
- 矩阵的加法和减法(Addition and Subtraction of Matrices)
- 矩阵划分(Division of Matrices)
- 矩阵的标量运算(Scalar Operations of Matrices)
- 矩阵的转置(Transpose of a Matrix)
- 连接矩阵(Concatenating Matrices)
- 矩阵乘法(Matrix Multiplication)
- 矩阵的行列式(Determinant of a Matrix)
- 逆矩阵(Inverse of a Matrix)
Differential
MATLAB提供了用于计算符号导数的diff命令。 在最简单的形式中,您将要区分为diff命令的函数作为参数传递。
例如,让我们计算函数f(t)= 3t 2 + 2t -2的导数
例子 (Example)
创建一个脚本文件并在其中键入以下代码 -
syms t
f = 3*t^2 + 2*t^(-2);
diff(f)
编译并执行上述代码时,会产生以下结果 -
ans =
6*t - 4/t^3
以下是Octave相当于上面的计算 -
pkg load symbolic
symbols
t = sym("t");
f = 3*t^2 + 2*t^(-2);
differentiate(f,t)
Octave执行代码并返回以下结果 -
ans =
-(4.0)*t^(-3.0)+(6.0)*t
基本分化规则的验证
让我们简要说明用于区分函数的各种方程或规则并验证这些规则。 为此,我们将f'(x)表示为一阶导数,f“(x)表示二阶导数。
以下是差异化的规则 -
Rule 1
对于任何函数f和g以及任何实数a和b是函数的导数 -
h(x) = af(x) + bg(x)相对于x由下式给出 -
h'(x) = af'(x) + bg'(x)
Rule 2
sum规则表明如果f和g是两个函数,f'和g'分别是它们的导数,那么,
( f + g)' = f' + g'
(f - g)' = f' - g'
Rule 3
product规则规定如果f和g是两个函数,f'和g'分别是它们的导数,那么,
(fg)' = f'.g + g'.f
Rule 4
quotient规则指出如果f和g是两个函数,f'和g'分别是它们的导数,那么,
(f/g)' = (f'.g - g'.f)/g 2
Rule 5
polynomial或基本幂次规则表明,如果y = f(x) = x n ,则f' = n. x (n-1) f' = n. x (n-1)
该规则的直接结果是任何常数的导数为零,即,如果y = k ,则任何常数
f' = 0
Rule 6
chain规则指出函数h(x) = f(g(x))的函数相对于x的导数是,
h'(x)= f'(g(x)).g'(x)
例子 (Example)
创建一个脚本文件并在其中键入以下代码 -
syms x
syms t
f = (x + 2)*(x^2 + 3)
der1 = diff(f)
f = (t^2 + 3)*(sqrt(t) + t^3)
der2 = diff(f)
f = (x^2 - 2*x + 1)*(3*x^3 - 5*x^2 + 2)
der3 = diff(f)
f = (2*x^2 + 3*x)/(x^3 + 1)
der4 = diff(f)
f = (x^2 + 1)^17
der5 = diff(f)
f = (t^3 + 3* t^2 + 5*t -9)^(-6)
der6 = diff(f)
运行该文件时,MATLAB显示以下结果 -
f =
(x^2 + 3)*(x + 2)
der1 =
2*x*(x + 2) + x^2 + 3
f =
(t^(1/2) + t^3)*(t^2 + 3)
der2 =
(t^2 + 3)*(3*t^2 + 1/(2*t^(1/2))) + 2*t*(t^(1/2) + t^3)
f =
(x^2 - 2*x + 1)*(3*x^3 - 5*x^2 + 2)
der3 =
(2*x - 2)*(3*x^3 - 5*x^2 + 2) - (- 9*x^2 + 10*x)*(x^2 - 2*x + 1)
f =
(2*x^2 + 3*x)/(x^3 + 1)
der4 =
(4*x + 3)/(x^3 + 1) - (3*x^2*(2*x^2 + 3*x))/(x^3 + 1)^2
f =
(x^2 + 1)^17
der5 =
34*x*(x^2 + 1)^16
f =
1/(t^3 + 3*t^2 + 5*t - 9)^6
der6 =
-(6*(3*t^2 + 6*t + 5))/(t^3 + 3*t^2 + 5*t - 9)^7
以下是Octave相当于上面的计算 -
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym("x");
t = sym("t");
f = (x + 2)*(x^2 + 3)
der1 = differentiate(f,x)
f = (t^2 + 3)*(t^(1/2) + t^3)
der2 = differentiate(f,t)
f = (x^2 - 2*x + 1)*(3*x^3 - 5*x^2 + 2)
der3 = differentiate(f,x)
f = (2*x^2 + 3*x)/(x^3 + 1)
der4 = differentiate(f,x)
f = (x^2 + 1)^17
der5 = differentiate(f,x)
f = (t^3 + 3* t^2 + 5*t -9)^(-6)
der6 = differentiate(f,t)
Octave执行代码并返回以下结果 -
f =
(2.0+x)*(3.0+x^(2.0))
der1 =
3.0+x^(2.0)+(2.0)*(2.0+x)*x
f =
(t^(3.0)+sqrt(t))*(3.0+t^(2.0))
der2 =
(2.0)*(t^(3.0)+sqrt(t))*t+((3.0)*t^(2.0)+(0.5)*t^(-0.5))*(3.0+t^(2.0))
f =
(1.0+x^(2.0)-(2.0)*x)*(2.0-(5.0)*x^(2.0)+(3.0)*x^(3.0))
der3 =
(-2.0+(2.0)*x)*(2.0-(5.0)*x^(2.0)+(3.0)*x^(3.0))+((9.0)*x^(2.0)-(10.0)*x)*(1.0+x^(2.0)-(2.0)*x)
f =
(1.0+x^(3.0))^(-1)*((2.0)*x^(2.0)+(3.0)*x)
der4 =
(1.0+x^(3.0))^(-1)*(3.0+(4.0)*x)-(3.0)*(1.0+x^(3.0))^(-2)*x^(2.0)*((2.0)*x^(2.0)+(3.0)*x)
f =
(1.0+x^(2.0))^(17.0)
der5 =
(34.0)*(1.0+x^(2.0))^(16.0)*x
f =
(-9.0+(3.0)*t^(2.0)+t^(3.0)+(5.0)*t)^(-6.0)
der6 =
-(6.0)*(-9.0+(3.0)*t^(2.0)+t^(3.0)+(5.0)*t)^(-7.0)*(5.0+(3.0)*t^(2.0)+(6.0)*t)
指数,对数和三角函数的导数
下表提供了常用指数函数,对数函数和三角函数的导数 -
| 功能 | 衍生物 |
|---|---|
| c ax | c ax .ln ca(ln是自然对数) |
| e x | e x |
| ln x | 1/x |
| ln c x | 1/x.ln c |
| x x | x x 。(1 + ln x) |
| sin(x) | cos(x) |
| cos(x) | -sin(x) |
| tan(x) | sec 2 (x),或1/cos 2 (x),或1 + tan 2 (x) |
| cot(x) | -csc 2 (x),或-1/sin 2 (x),或 - (1 + cot 2 (x)) |
| sec(x) | sec(x).tan(x) |
| csc(x) | -csc(x).cot(x) |
例子 (Example)
创建一个脚本文件并在其中键入以下代码 -
syms x
y = exp(x)
diff(y)
y = x^9
diff(y)
y = sin(x)
diff(y)
y = tan(x)
diff(y)
y = cos(x)
diff(y)
y = log(x)
diff(y)
y = log10(x)
diff(y)
y = sin(x)^2
diff(y)
y = cos(3*x^2 + 2*x + 1)
diff(y)
y = exp(x)/sin(x)
diff(y)
运行该文件时,MATLAB显示以下结果 -
y =
exp(x)
ans =
exp(x)
y =
x^9
ans =
9*x^8
y =
sin(x)
ans =
cos(x)
y =
tan(x)
ans =
tan(x)^2 + 1
y =
cos(x)
ans =
-sin(x)
y =
log(x)
ans =
1/x
y =
log(x)/log(10)
ans =
1/(x*log(10))
y =
sin(x)^2
ans =
2*cos(x)*sin(x)
y =
cos(3*x^2 + 2*x + 1)
ans =
-sin(3*x^2 + 2*x + 1)*(6*x + 2)
y =
exp(x)/sin(x)
ans =
exp(x)/sin(x) - (exp(x)*cos(x))/sin(x)^2
以下是Octave相当于上面的计算 -
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym("x");
y = Exp(x)
differentiate(y,x)
y = x^9
differentiate(y,x)
y = Sin(x)
differentiate(y,x)
y = Tan(x)
differentiate(y,x)
y = Cos(x)
differentiate(y,x)
y = Log(x)
differentiate(y,x)
% symbolic packages does not have this support
%y = Log10(x)
%differentiate(y,x)
y = Sin(x)^2
differentiate(y,x)
y = Cos(3*x^2 + 2*x + 1)
differentiate(y,x)
y = Exp(x)/Sin(x)
differentiate(y,x)
Octave执行代码并返回以下结果 -
y =
exp(x)
ans =
exp(x)
y =
x^(9.0)
ans =
(9.0)*x^(8.0)
y =
sin(x)
ans =
cos(x)
y =
tan(x)
ans =
1+tan(x)^2
y =
cos(x)
ans =
-sin(x)
y =
log(x)
ans =
x^(-1)
y =
sin(x)^(2.0)
ans =
(2.0)*sin(x)*cos(x)
y =
cos(1.0+(2.0)*x+(3.0)*x^(2.0))
ans =
-(2.0+(6.0)*x)*sin(1.0+(2.0)*x+(3.0)*x^(2.0))
y =
sin(x)^(-1)*exp(x)
ans =
sin(x)^(-1)*exp(x)-sin(x)^(-2)*cos(x)*exp(x)
计算高阶导数
为了计算函数f的更高导数,我们使用语法diff(f,n) 。
让我们计算函数y = f(x)= x .e -3x的二阶导数
f = x*exp(-3*x);
diff(f, 2)
MATLAB执行代码并返回以下结果 -
ans =
9*x*exp(-3*x) - 6*exp(-3*x)
以下是Octave相当于上面的计算 -
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym("x");
f = x*Exp(-3*x);
differentiate(f, x, 2)
Octave执行代码并返回以下结果 -
ans =
(9.0)*exp(-(3.0)*x)*x-(6.0)*exp(-(3.0)*x)
例子 (Example)
在这个例子中,让我们解决一个问题。 假设函数y = f(x) = 3 sin(x) + 7 cos(5x) 。 我们必须弄清楚等式f" + f = -5cos(2x)成立。
创建一个脚本文件并在其中键入以下代码 -
syms x
y = 3*sin(x)+7*cos(5*x); % defining the function
lhs = diff(y,2)+y; %evaluting the lhs of the equation
rhs = -5*cos(2*x); %rhs of the equation
if(isequal(lhs,rhs))
disp('Yes, the equation holds true');
else
disp('No, the equation does not hold true');
end
disp('Value of LHS is: '), disp(lhs);
运行该文件时,它显示以下结果 -
No, the equation does not hold true
Value of LHS is:
-168*cos(5*x)
以下是Octave相当于上面的计算 -
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym("x");
y = 3*Sin(x)+7*Cos(5*x); % defining the function
lhs = differentiate(y, x, 2) + y; %evaluting the lhs of the equation
rhs = -5*Cos(2*x); %rhs of the equation
if(lhs == rhs)
disp('Yes, the equation holds true');
else
disp('No, the equation does not hold true');
end
disp('Value of LHS is: '), disp(lhs);
Octave执行代码并返回以下结果 -
No, the equation does not hold true
Value of LHS is:
-(168.0)*cos((5.0)*x)
找到曲线的最大值和最小值
如果我们正在搜索图的局部最大值和最小值,我们基本上是在特定位置的函数图上寻找最高点或最低点,或者是符号变量的特定值范围。
对于函数y = f(x),图形上具有零斜率的图上的stationary points称为stationary points 。 换句话说,静止点是f'(x)= 0的位置。
为了找到我们区分的函数的平稳点,我们需要将导数设置为零并求解方程。
例子 (Example)
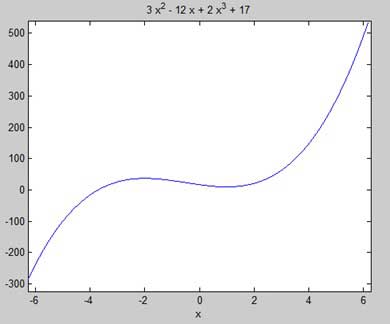
让我们找到函数f(x)= 2x 3 + 3x 2 - 12x + 17的平稳点
采取以下步骤 -
First let us enter the function and plot its graph.
syms x
y = 2*x^3 + 3*x^2 - 12*x + 17; % defining the function
ezplot(y)
MATLAB执行代码并返回以下图表 -
以下是上述示例的Octave等效代码 -
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym('x');
y = inline("2*x^3 + 3*x^2 - 12*x + 17");
ezplot(y)
print -deps graph.eps
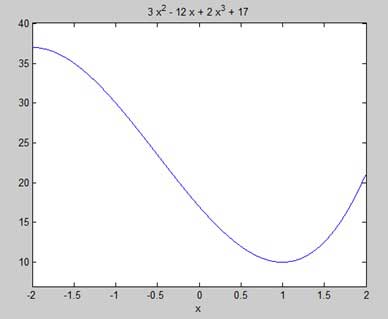
Our aim is to find some local maxima and minima on the graph, so let us find the local maxima and minima for the interval [-2, 2] on the graph.
syms x
y = 2*x^3 + 3*x^2 - 12*x + 17; % defining the function
ezplot(y, [-2, 2])
MATLAB执行代码并返回以下图表 -
以下是上述示例的Octave等效代码 -
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym('x');
y = inline("2*x^3 + 3*x^2 - 12*x + 17");
ezplot(y, [-2, 2])
print -deps graph.eps
Next, let us compute the derivative.
g = diff(y)
MATLAB执行代码并返回以下结果 -
g =
6*x^2 + 6*x - 12
这是Octave相当于上面的计算 -
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym("x");
y = 2*x^3 + 3*x^2 - 12*x + 17;
g = differentiate(y,x)
Octave执行代码并返回以下结果 -
g =
-12.0+(6.0)*x+(6.0)*x^(2.0)
Let us solve the derivative function, g, to get the values where it becomes zero.
s = solve(g)
MATLAB执行代码并返回以下结果 -
s =
1
-2
以下是Octave相当于上面的计算 -
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym("x");
y = 2*x^3 + 3*x^2 - 12*x + 17;
g = differentiate(y,x)
roots([6, 6, -12])
Octave执行代码并返回以下结果 -
g =
-12.0+(6.0)*x^(2.0)+(6.0)*x
ans =
-2
1
This agrees with our plot. So let us evaluate the function f at the critical points x = 1, -2. 我们可以使用subs命令替换符号函数中的值。
subs(y, 1), subs(y, -2)
MATLAB执行代码并返回以下结果 -
ans =
10
ans =
37
以下是Octave相当于上面的计算 -
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym("x");
y = 2*x^3 + 3*x^2 - 12*x + 17;
g = differentiate(y,x)
roots([6, 6, -12])
subs(y, x, 1), subs(y, x, -2)
ans =
10.0
ans =
37.0-4.6734207789940138748E-18*I
因此,函数f(x)= 2x 3 + 3x 2 - 12x + 17的最小值和最大值在区间[-2,2]中是10和37。
求解微分方程
MATLAB提供了用于象征性地求解微分方程的dsolve命令。
用于查找单个方程的解的dsolve命令的最基本形式是
dsolve('eqn')
其中eqn是用于输入eqn的文本字符串。
它返回一个符号解决方案,其中包含一组MATLAB标记C1,C2等的任意常量。
您还可以指定问题的初始条件和边界条件,如下所示,以逗号分隔的列表为 -
dsolve('eqn','cond1', 'cond2',…)
出于使用dsolve命令的目的,使用derivatives are indicated with a D 。 例如,输入f'(t)= -2 * f + cost(t)之类的等式作为 -
'Df = -2*f + cos(t)'
通过D导数的顺序表示更高的导数。
例如,方程f“(x)+ 2f'(x)= 5sin3x应输入 -
'D2y + 2Dy = 5*sin(3*x)'
让我们举一个简单的一阶微分方程的例子:y'= 5y。
s = dsolve('Dy = 5*y')
MATLAB执行代码并返回以下结果 -
s =
C2*exp(5*t)
让我们将二阶微分方程的另一个例子作为:y“ - y = 0,y(0)= -1,y'(0)= 2。
dsolve('D2y - y = 0','y(0) = -1','Dy(0) = 2')
MATLAB执行代码并返回以下结果 -
ans =
exp(t)/2 - (3*exp(-t))/2
如果你对这篇内容有疑问,欢迎到本站社区发帖提问 参与讨论,获取更多帮助,或者扫码二维码加入 Web 技术交流群。

绑定邮箱获取回复消息
由于您还没有绑定你的真实邮箱,如果其他用户或者作者回复了您的评论,将不能在第一时间通知您!
发布评论